Internet Architecture
We all know that internet evolved with a great pace. One of the main reason for this rapid evolution is that most application developers don't have to write programs that run on network core devices like routers, link-layer switches etc as the 'Internet Architecture' provides certain services to applications.
When an application developer decides to build an application he will most probably choose one of the internet's major architectural paradigms:
- Client-Server Architecture: In a client-server architecture a 'server' services requests from 'clients'. The web is a famous application based on client-server architecture in which a web browser like Chrome requests data from a server. One distinct feature of this paradigm is that two clients(browsers) do not communicate directly with each other. Some other applications based on client-server architecture are FTP(File Transfer Protocol), e-mail etc.
- Peer-to-Peer(P2P) Architecture: In P2P architecture two hosts (peers) communicate directly with each other and are not dependent on servers. The two hosts are mainly user controlled. Eg: BitTorrent, Skype.
| Client-Server VS Peer-to-Peer Architecture |
However some applications have hybrid architecture consisting of both client-server and P2P. Many instant messaging applications use servers to track IP addresses but the messages are exchanged directly without going through intermittent servers.
Process:
Two hosts communicate with each other using 'processes' which are nothing but programs that exchange 'messages'. A sending process generates a message and sends it into the network. From now on wards it is the responsibility of network services to deliver the message to the receiving host or particularly receiving process, which in turn takes certain actions depending on the message received and probably responds with a message.
Socket:
A process sends message into, and receives message from, the network through a software interface called 'socket'. A process is analogous to a house and socket to it's door. The sending house assumes that there is an architecture that delivers the message to destination house.
| Socket |
Addressing:
To deliver a message to the destination, two parameters need to be specified:
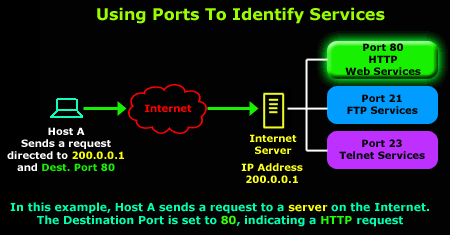
- Address of the host: In the internet the host is identified by an IP address.
- Port Number: It identifies the exact process as a host may be running several processes of several network applications. For example, a web server is identified by port number 80 and an e-mail server is identified by port number 25.
****

No comments:
Post a Comment