Cookies
It's time for cookies!
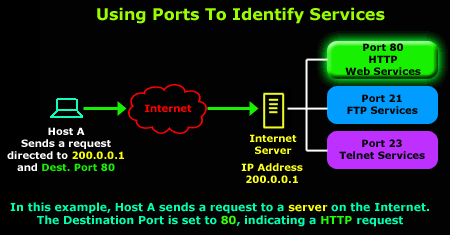
It is always favorable for websites to keep track of their visitors so that they can either restrict their usage or deliver content according to their previous search history. Here the role of "Cookies" come into play which are defines in ' RFC 6265 '. As HTTP is a stateless protocol, cookies create a user session layer on top HTTP.
Cookie technology has four components:
- A cookie header line in HTTP request message.
- A cookie header line in HTTP response message.
- A cookie file managed by user's browser.
- A backend database at the website.
Cookie Mechanism:

- Suppose Mr X is visiting flipkart.com for the first time.
- When the flipkart server receives the request it assigns an unique identification number to Mr X and makes an entry in its backend database which is indexed by the identification number.
- Then the flipkart server sends an HTTP response message which includes " Set-cookie: " header containing the identification number.
- When Mr X's browser receives the response it interprets the set-cookie header and appends the data to the special cookie file it maintains.
- The data includes hostname of the server and the identification number.
- Every time Mr X's computer wants to send a request to flipkart server, the browser adds the " Cookie: " header in its request HTTP message.
- The server performs a lookup for Mr.X's ID and delivers content accordingly.
- This is how the flipkart server keeps a track of Mr.X's activity at the site.
- Although the site does not have Mr. X's name, it does know what he has been browsing and at what times!
- Now if Mr.X registers by providing his full name, credit-card details, location(address) then the server can associate all this information with the ID. (The site now has a lot of information about Mr.X !!)
Although cookies simplify internet usage they can be controversial !!

$$$$$$$