Internet Jargon
Internet:
Internet is a global computer network which provides services to various applications by using standardized protocols.
 |
| Internet |
End Systems:
- End systems are devices like laptop,desktop,mobile etc which sit at the end of computer networks and run various applications like email,web browser program, web server programs etc.
- End systems are also referred to as hosts.
 |
| End Systems |
- There are two types of hosts:clients and servers
- The clients can access data or services provided by the server.
 |
| Clients and Servers |
Communication Links:
Communication links are physical media like optic fiber,coaxial cable or radio spectrum which connects two communicating devices.
 |
| Radio Spectrum for Communication |
 |
| Network Cables |
Transmission Rate:
- Transmission Rate is defined as number of bits transmitted in unit time.
Packets:
- When data is to be sent through a communication link from one end system to the other it is segmented into packets.
- Every packet has header bits which contain information about the destination where it is to be sent.
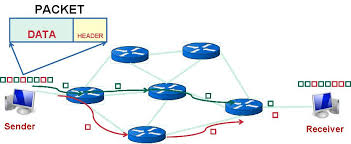
Packet Switch:
A packet switch takes packet arriving at one of its incoming communication link and sends it to one of its outbound link according to destination address.
 |
| Packet Switch |
Route/Path:
Route or Path is the sequence of communication links and packet switches traversed by a packet from sending end system to receiving end system.
ISP(Internet Service Provider):
According to Wikipedia ISP(Internet Service Provider) is an organization that provides services for accessing, using, or participating in the Internet.
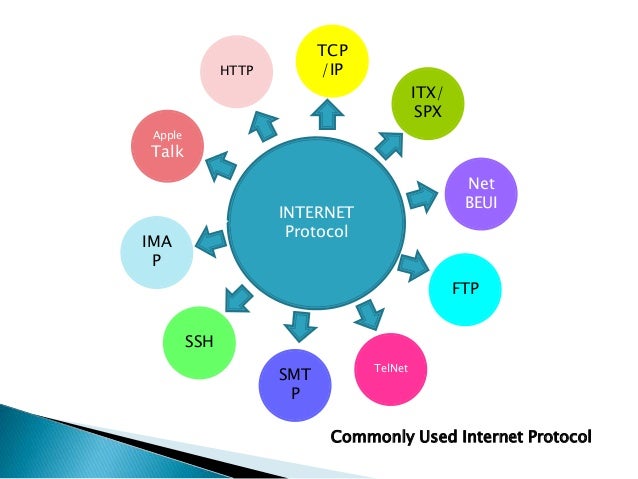
Protocols:
- Protocols define the format and order of messages exchanged between two communicating devices.
- Internet standard protocols are developed by IETF(Internet Engineering Task Force).
- The standard documents are called RFCs (Requests For Comments).
Access Networks:
- An access network is a type of network which physically connects an end system to the immediate router (also known as the “edge router”) on a path from the end system to any other distant end system.
- Example of access networks are DSL(Digital Subscriber Link), FTTH(Fiber To The Home), HFC(Hybrid Fiber Coaxial Network) etc.








